Population of Canada

Top left: The Quebec City–Windsor Corridor is the most densely inhabited and heavily industrialized region accounting for nearly 50 percent of the total population[1]
Canada ranks 36th by population among countries of the world, comprising about 0.5% of the world's total,[2] with more than 40 million Canadians as of 2024.[3][4] Despite being the second-largest country by total area (fourth-largest by land area), the vast majority of the country is sparsely inhabited, with most of its population south of the 55th parallel north. Just over 60 percent of Canadians live in just two provinces: Ontario and Quebec. Though Canada's overall population density is low, many regions in the south, such as the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, have population densities higher than several European countries. Canada has six population centres with more than one million people: Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton and Ottawa.
The large size of Canada's north, which is currently not arable, and thus cannot support large human populations, significantly lowers the country's carrying capacity. In 2021, the population density of Canada was 4.2 people per square kilometre.[5]
The historical growth of Canada's population is complex and has been influenced in many different ways, such as Indigenous populations, expansion of territory, and human migration. Immigration has been, and remains, the most important factor in Canada's population growth.[6] The 2021 Canadian census counted a total population of 36,991,981, an increase of around 5.2 per cent over the 2016 figure.[7][8] Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 per cent overall growth.[9]
Historical population overview
[edit]Indigenous peoples
[edit]
A variety of estimations have been postulated for the Indigenous population in what is now Canada prior to European contact.[11] Estimates of this population during the late 15th century range between 200,000[12] and two million,[13] with a figure of 500,000 currently accepted by Canada's Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples.[14] Although not without conflict, European Canadians' early interactions with First Nations and Inuit populations were relatively peaceful.[15] However repeated outbreaks of European infectious diseases such as influenza, measles and smallpox (to which they had no natural immunity),[16] combined with other effects of European contact, resulted in a twenty-five per cent to eighty per cent Indigenous population decrease post-contact.[12] Roland G Robertson suggests that during the late 1630s, smallpox killed over half of the Wyandot (Huron), who controlled most of the early North American fur trade in the area of New France.[17] In 1822 the Indigenous Canadian population, excluding the Métis, was estimated as 283,500 people.[18] In 1871 there was an enumeration of the Indigenous population within the limits of Canada at the time, showing a total of only 102,358 individuals.[19] In 1885 the number of Indigenous people in Canada was reported as 131,952 individuals.[20] From 2006 to 2016, the Indigenous population has grown by 42.5 per cent, four times the national rate.[21] The Indigenous population representing 5 percent or 1.8 million individuals, grew by 9.4 percent compared to the non-Indigenous population, which grew by 5.3 percent from 2016 to 2021.[22] The 2021 Census data reveals that there are over 1. 8 million Indigenous people in Canada, comprising 5. 0% of the overall Canadian population, a slight increase from 4. 9% in 2016,[23]
New France
[edit]The European population grew slowly under French rule,[24] thus remained relatively low as growth was largely achieved through natural births, rather than by immigration.[25] Most of the French were farmers, and the rate of natural increase among the settlers themselves was very high.[26] The women had about 30 per cent more children than comparable women who remained in France.[27] Demographer Yves Landry says, "Canadians had an exceptional diet for their time."[27] The 1666 census of New France was the first census conducted in North America.[28] It was organized by Jean Talon, the first Intendant of New France, between 1665 and 1666.[28] According to Talon's census there were 3,215 people in New France, comprising 538 separate families.[29] The census showed a great difference in the number of men at 2,034 versus 1,181 women.[29] By the early 1700s the New France settlers were well established along the Saint Lawrence River and Acadian Peninsula with a population around 15,000 to 16,000.[30] Mainly due to natural increase and modest immigration from Northwest France (Brittany, Normandy, Île-de-France, Poitou-Charentes and Pays de la Loire) the population of New France increased to 55,000 according to the last French census of 1754.[31] This was an increase from 42,701 in 1730.[32]
British Canada
[edit]
During the late 18th and early 19th century Canada under British rule experienced strong population growth. In the wake of the 1775 invasion of Canada by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, approximately 60,000 of the 80,000 Americans loyal to the Crown, designated later as United Empire Loyalists fled to British North America, a large portion of whom migrated to Nova Scotia and New Brunswick (separated from Nova Scotia) in 1784.[33] Although the exact numbers cannot be certain because of unregistered migration[34] At least 20,000 went to Nova Scotia, 14,000 to New Brunswick; 1,500 to PEI and 6,000 to Ontario(13,000 including 5,000 blacks went to England and 5,500 to the Caribbean). For the rest of the 1780s additional immigrants arrived from the south. From 1791 An additional 30,000 Americans, called "Late Loyalists", were lured into Ontario in the 1790s by the promise of land and swearing loyalty to the Crown.[35] As a result of the period known as the Great Migration by 1831, Lower Canada's population had reached approximately 553,000, with Upper Canada reaching about 237,000 individuals.[36] The Great Famine of Ireland of the 1840s had significantly increased the pace of Irish immigration to Prince Edward Island and the Province of Canada, peaking in 1847 with 100,000 distressed individuals.[37] By 1851, the population of the Maritime colonies also reached roughly 533,000 (277,000 in Nova Scotia, 194,000 in New Brunswick and 62,000 in Prince Edward Island).[38] To the west British Columbia had about 55,000 individuals by 1851.[38] Beginning in the late 1850s, the immigration of Chinese into the Colony of Vancouver Island and Colony of British Columbia peaked with the onset of the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush.[39] By 1861, as a result of natural births and the Great Migration of Canada from the British Isles, the Province of Canada population increased to 3.1 million inhabitants.[38] Newfoundland's population by 1861 reached approximately 125,000 individuals.[38]
Post-confederation
[edit]The population has increased every year since the establishment of the Dominion of Canada in 1867; however, the population of Newfoundland was not included prior to its entry into confederation as Canada's tenth province in 1949.[40][41] The first national census of the country was taken in 1871, with a population count around 3,689,000.[42] The year with the least population growth (in real terms) was 1882–1883, when only 30,000 new individuals were enumerated.[41]

The 1911 census was a detailed enumeration of the population showing a count of 7,206,643 individuals.[43] This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315.[44] The year with the most population growth was during the peak of the Post-World War II baby boom in 1956–1957, when the population grew by over 529,000, in a single twelve-month period.[41] The Canadian baby boom, defined as the period from 1947 to 1966, saw more than 400,000 babies born annually.[45] The 1996 census recorded a total population of 28,846,761.[46] This was a 5.7% increase over the 1991 census of 27,296,859.[46] The 2001 census had a total population count of 30,007,094.[47] In contrast, the official Statistics Canada population estimate for 2001 was 31,021,300.[48]
Canada's total population enumerated by the 2006 census was 31,612,897.[49] This count was lower than the official 1 July 2006 population estimate of 32,623,490 people.[49] Ninety per cent of the population growth between 2001 and 2006 was concentrated in the main metropolitan areas.[50] The 2011 census was the fifteenth decennial census with a total population count of 33,476,688 up 5.9% from 2006. On average, censuses have been taken every five years since 1905. Censuses are required to be taken at least every ten years as mandated in section 8 of the Constitution Act, 1867.[51]
Components of population growth
[edit]A population estimate for 2022 put the total number of people in Canada at 38,232,593.[52]
Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022.[53]
- One birth every 1 minute
- One death every 2 minutes
- One net migrant every 2 minutes
- Net gain of one person every 2 minutes
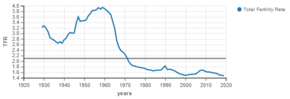
In 2010, Canada's annual population growth rate was 1.238%, or a daily increase of 1,137 individuals.[41] Between 1867 and 2009 Canada's population grew by 979%.[41] Canada had the highest net migration rate (0.61%) of all G-8 member countries between 1994 and 2004.[41] Natural growth accounts for an annual increase of 137,626 persons, at a yearly rate of 0.413%.[41] Between 2001 and 2006, there were 1,446,080 immigrants and 237,418 emigrants, resulting in a net migration of just over 1.2 million people.[41] Since 2001 until 2010, immigration has ranged between 221,352 and 262,236 immigrants per annum.[54]
In 2023, Canada's population jumped by over 1 million people for the first time in the country's history. The population now stands at 39.5 million and is set to pass the 40 million mark later this year. The population growth has largely been fuelled by migrants who have been brought into the country to ease labour shortages.[55]
Population by years
[edit]Prior to Canadian confederation in 1867 the population counts reflected only the former colonies and settlements and not the country to be as a whole with Indigenous nations separated.[56]
Ephemeral European settlements
[edit]| Year | Area/colony | Population | Notes[57] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | L'Anse aux Meadows (Newfoundland) |
30 to 160 | Archaeological evidence of a short-lived Norse settlement was found at L'Anse aux Meadows, on the northernmost tip of the island of Newfoundland (carbon dating estimate 990–1050 AD.[58]) There is no record of how many men and women lived at the site at any given time, however archaeological evidence of the dwellings suggest it had the capacity of supporting 30 to 160 individuals.[59] |
| 1541 | Cap-Rouge (Quebec City) |
400 | Jacques Cartier established Charlesbourg-Royal at Cap-Rouge on his third voyage. Even though scurvy was cured through the Indigenous remedy (Thuja occidentalis infusion), the impression left is of a general misery with the effort being abandoned.[60] During the winter 35 of Cartier's men perished.[60] |
| 1543 | Cap-Rouge (Quebec City) |
200 | In 1542, Jean-François Roberval tried to re-invigorate the Charlesbourg-Royal colony at Cap-Rouge which Roberval renamed France-Roy, however after a set of disastrous winters the effort was abandoned.[61] En route to Charlesbourg-Royal, Roberval had abandoned his near-relative Marguerite de La Rocque with her lover on the "Isle of Demons" (now called Harrington Island), in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, as punishment for their affair.[62] The young man, their servant and baby died, but Marguerite survived to be rescued by fishermen and returned to France two years later.[62] |
| 1583 | St. John Bay (Newfoundland) |
260 | Humphrey Gilbert with 260 men planned a settlement; however, during exploration of the coast line a ship was lost containing many of the prospective colonists and their provisions.[63] |
| 1598 | Sable Island (Nova Scotia) |
50 | Marquis de La Roche-Mesgouez and 40 convicts (peasants and beggars) with 10 soldiers settled on Sable Island, but this colonization attempt failed, culminating in a revolt with only 11 survivors evacuated.[64][65] |
| 1600 | Tadoussac (Quebec) |
16 | François Gravé Du Pont with 16 men built a fur trading post at Tadoussac; however, only five of the men survived the winter before returning to France.[65] |
| 1604 | Saint Croix (Maine) |
79 | The St. Croix settlement of Maine was the first real attempt at a year-round base of operation in New France. The expedition was led by Pierre Du Gua de Monts with 79 settlers including François Gravé Du Pont, Royal cartographer Samuel de Champlain, the Baron de Poutrincourt, apothecary Louis Hébert, a priest Nicolas Aubry, and Mathieu de Costa a linguist.[66] The St. Croix settlement was abandoned the following summer for a new habitation at Port-Royal after 35 died of scurvy.[67] |
Former colonies and territories
[edit]The first in date of the Colonies which became successful, and which consequently marked the starting point of European settlements on what would be Canada , was the foundation of Port Royal, Acadia.[68] List of censuses.[69][70]
| Year | Area/colony | Population[71][72][73] | Notes[56] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1605 | Port Royal (Nova Scotia) |
44 | The 44 colonists are surviving members of 79 from the now abandoned St. Croix settlement of Maine.[65] However, the habitation at Port-Royal was also abandoned and left in the care of the local Mi'kmaq.[67] The settlement was later moved upstream and to the south bank of the Annapolis River, keeping the name Port-Royal and becoming the capital of Acadia.[74] |
| 1608 | Quebec City | 28 | Samuel de Champlain establishes the colony with 28 settlers.[65] Half of the men that winter the first year die of scurvy or starvation.[75] Nevertheless, new settlers arrive resulting in Quebec being the first permanent settlement, and also the capital of, the French colony of Canada. |
| 1610 | Cuper's Cove (Newfoundland) |
40 | The Newfoundland Colony is established by John Guy his brother Phillip and his brother-in-law William Colston with 39 colonists who spend the winter of 1610–1611 at Cuper's Cove.[76] By the fall of 1613 sixteen structures are completed by about 60 settlers on the site.[77][78] As England tried to create a foothold in the north, other settlements were established at Bristol's Hope, Renews, New Cambriol, South Falkland and Avalon, an area that became known as the English Shore. However the majority of the population did not stay year round returning in the spring of each year. Over the next 100 years the English colonies of Newfoundland grew very slowly, and had only 3,000 permanent residents by the 1720s.[79] |
| 1629 | Quebec city | 117 | *90 wintering belonged to Kirke's English Expedition that had captured the city.[80] Under brief British control the city begins to grow and be fortified.[81] Prior to 1632 only eight births were recorded among the 60 to 70 permanent European settlers.[81][82] The first European child born in Quebec had been Hélène Desportes, in 1620.[83] |
| 1641 | New France | 240 | De facto population of Canada (New France) and Acadia, now situated partly in the future United States.[82] |
| 1642 | Fort Ville-Marie (Old Montreal) |
50 | New colony with the majority of immigrants coming directly from France led by Paul de Chomedey and Jeanne Mance, a lay woman.[84] |
| 1666 | Canada (New France) | 3,215 | The 1660s marked the only real "wave" of French settlers arriving until the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713.[85] Following the initial wave of French settlers natural growth was the main contributing factor to population growth.[81] Quebec city 2,100, Trois-Rivières 455, Montreal 655. (Comprising 528 families with 2,034 men and 1,181 women. Professionals included 3 notaries, 3 schoolmasters, 3 locksmiths, 4 bailiffs, 5 surgeons, 5 bakers, 8 barrel makers, 9 millers, 18 official merchants, 27 joiners, and 36 carpenters.)[56] |
| 1677 | Indigenous Nations |
10,750 | Estimated Indigenous population in and around New France territory 10,750, including 2,150 warriors. (Mohawks 5 villages, 96 lodges, 300 warriors – Oneidas 1 village, 100 lodges, 200 warriors – Onondagas 2 villages, 164 lodges, 350 warriors – Cayugas 3 villages, 100 lodges, 300 warriors – Senecas 4 villages, 324 lodges, 1,000 warriors).[19] |
| 1679 | Acadia | 515 | Majority are from the Poitou region of France. |
| 1681 | New France | 9,677 | New France sees new settlements develop as residents leave Quebec City (population 1,345) and Trois-Rivières (150) with Montreal gaining influence (population 1,418).[56] |
| 1687 | Newfoundland | 663 | French population only. |
| 1695 | New France | 13,639 | Population of Saint John River New Brunswick 49. |
| 1698 | New France | 15,355 | English population of Newfoundland at the time 1,500. |
18th century
[edit]| Year | Area/colony | Population[73][86] | Notes[56] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1705 | Newfoundland | 520 | French population only |
| 1706 | New France | 16,417 | Covering territory that is now situated partly in the United States of America and partly in Canada. |
| 1712 | New France | 18,440 | Married – men 2,786, women 2,588. Unmarried – males 6,716, females 6,350.[56] |
| 1718 | New France | 22,983 | Married – men 3,662, women 3,926. Unmarried – males 7,911, females 7,484.[56] |
| 1720 | St.John Island (Prince Edward Island) |
100 | 17 families |
| 1730 | New France | 33,682 | Married – men 6,050, women 5,728. Unmarried – males 11,314, females 10,590.[56] |
| 1736 | Indigenous Nations |
17,575 | Estimated population of First Nations in New France that are now within Canada – Abenakis 2,950 – Algonquins, Ottawas, Potawatomi, Saulteaux and Crees 11,475 – Wyandot-Huron 1,300 – Iroquois 1,850.[19] |
| 1737 | New France | 39,970 | Married – men 7,378, women 6,804. Unmarried – males 13,330, females 12,458.[56] |
| 1741 | Newfoundland | 6,000 | English population only. |
| 1749 | Nova Scotia | 2,544 | Married – men, 509; women 509. Unmarried – men, 660; women, 3. Children-boys, 228; girls, 216. Servants-men, 277; women, 142.[56] |
| 1749 | Île-Royale (Cape Breton) |
1,000 | French population only. |
| 1749 | Acadian Mainland (New Brunswick) | 1,000 | French population only. |
| 1749 | Acadian Peninsula | 13,000 | French population only. |
| 1749 | St. John Island (Prince Edward Island) |
1,000 | French population only. |
| 1752 | Acadia (non-French) | 4,203 | British and German population only. Men over sixteen years old, 574; women over sixteen years old, 607. Children boys, 1,899; children girls, 1,123. |
| 1760 | New France | 70,000 | Expulsion of the Acadians three-quarters of the Acadian population of 18,000 forcibly relocated between 1755 and 1764.[87] |
| 1765 | Province of Quebec (1763–91) | 69,810 | French and English populations. |
| 1775 | Province of Quebec (1763–91) | 90,000 | French and English populations. |
| 1785 | Newfoundland | 10,244 | French and English populations. |
| 1790 | Nova Scotia | 30,000 | French and English populations. |
| 1797 | St. John Island (Prince Edward Island) |
4,500 | French and English populations. |
19th century
[edit]| Year | Area/Province | Population[88] |
|---|---|---|
| 1806 | New Brunswick | 35,000 |
| 1806 | Prince Edward Island | 9,676 |
| 1806 | Upper Canada | 70,718 |
| 1806 | Lower Canada | 250,000 |
| 1806 | Newfoundland | 26,505 |
| 1807 | Nova Scotia | 65,000 |
| 1822 | Prince Edward Island | 24,600 |
| 1823 | Newfoundland | 52,157 |
| 1824 | Upper Canada | 150,066 |
| 1824 | New Brunswick | 74,176 |
| 1825 | Upper Canada | 157,923 |
| 1825 | Lower Canada | 479,288 |
| 1831 | Lower Canada | 553,134 |
| 1832 | Upper Canada | 263,554 |
| 1832 | Newfoundland | 59,280 |
| 1833 | Prince Edward Island | 32,292 |
| 1844 | Canada East | 697,084 |
| 1845 | Newfoundland | 96,295 |
| 1846 | Assiniboia (North-West Territories) | 4,871 |
| 1848 | Canada West | 725,879 |
| 1861 | Colony of Vancouver Island | 3,024 |
| 1869 | Newfoundland | 146,536 |
| 1871 | British Columbia | 36,247 |
| 1871 | Manitoba | 25,228 |
| 1871 | Ontario | 1,620,851 |
| 1871 | Quebec | 1,191,516 |
| 1871 | New Brunswick | 285,594 |
| 1871 | Nova Scotia | 387,800 |
| 1871 | Prince Edward Island | 94,021 |
| 1871 | Northwest Territories | 48,000 |
| Year | Canada as a whole | Population | Provinces/Area[19][18][20] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1822 | Indigenous population | 283,500 | British North America 283,500 |
| 1871 | Indigenous population | 102,358 | Prince Edward Island 323 – Nova Scotia 1,666 – New Brunswick 1,403 – Quebec 6,988 – Ontario 12,978 – British Columbia 23,000 – Rupert's Land 33,500 – Manitoba 500 and Labrador and the Arctic Watersheds 22,000 |
| 1885 | Indigenous population | 131,952 | Prince Edward Island 292 - Nova Scotia 2,197 - New Brunswick 1,524 - Quebec 12,023 - Ontario 16,892 - British Columbia 39,011 - Eastern Rupert's Land 4,016 - Manitoba and Northwest Territories 33,959 - Peace River district 2,038 - Athabaska district 8,000 - McKenzie district 7,000 - Labrador (Canadian interior) 1,000 - Arctic coast 4,000 |
Canada as a whole since confederation
[edit]
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Census data by years
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1822 | 283,500 | — |
| 1871 | 102,358 | −63.9% |
| 1881 | 108,547 | +6.0% |
| 1885 | 131,952 | +21.6% |
| 1901 | 147,941 | +12.1% |
| 1911 | 105,611 | −28.6% |
| 1921 | 114,083 | +8.0% |
| 1931 | 128,899 | +13.0% |
| 1941 | 160,937 | +24.9% |
| 1951 | 165,607 | +2.9% |
| 1961 | 220,121 | +32.9% |
| 1971 | 312,765 | +42.1% |
| 1981 | 491,460 | +57.1% |
| 1986 | 711,725 | +44.8% |
| 1991 | 1,016,340 | +42.8% |
| 1996 | 799,010 | −21.4% |
| 2001 | 976,305 | +22.2% |
| 2006 | 1,172,790 | +20.1% |
| 2011 | 1,400,690 | +19.4% |
| 2016 | 1,673,785 | +19.5% |
| 2021 | 1,807,250 | +8.0% |
| Source: Statistics Canada [19][91][92]: 5&6 [93]: 3 [94]: 1 [95]: 17 [96][97][98][99][100][101][18][20] Note: Population decline between 1991 and 1996 censuses attributed to change in criteria in census count; "the 1996 Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples used a more restrictive definition of Aboriginal".[102] | ||
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | 3,689,257 | — |
| 1881 | 4,324,810 | +17.2% |
| 1891 | 4,833,239 | +11.8% |
| 1901 | 5,371,315 | +11.1% |
| 1911 | 7,206,643 | +34.2% |
| 1921 | 8,787,949 | +21.9% |
| 1931 | 10,374,196 | +18.1% |
| 1941 | 11,506,655 | +10.9% |
| 1951 | 14,009,429 | +21.8% |
| 1961 | 18,238,247 | +30.2% |
| 1971 | 21,568,311 | +18.3% |
| 1976 | 22,992,604 | +6.6% |
| 1981 | 24,343,181 | +5.9% |
| 1986 | 25,309,331 | +4.0% |
| 1991 | 27,296,859 | +7.9% |
| 1996 | 28,846,761 | +5.7% |
| 2001 | 30,007,094 | +4.0% |
| 2006 | 31,612,897 | +5.4% |
| 2011 | 33,476,688 | +5.9% |
| 2016 | 35,151,728 | +5.0% |
| 2021 | 36,991,981 | +5.2% |
| [103][104][105][106][107][108][109][110][111] | ||
Data projections
[edit]In 2006, Statistics Canada projected for the decade 2021 to 2031 the population to grow by more than 5 million, or more than 10%.[112] Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 per cent overall growth.[9] The 2016 Canadian census counted a total population of 35.1 million,[7] or 1.5 million under the 2006 projection.
In October 2020, the Trudeau government announced its plans to bring in more than 1.2 million immigrants over the subsequent three years, to catch up to the high-growth scenario.[113]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 33,470,000 | — |
| 2016 | 36,540,000 | +9.2% |
| 2021 | 39,110,000 | +7.0% |
| 2026 | 41,750,000 | +6.8% |
| 2031 | 44,430,000 | +6.4% |
| 2036 | 47,130,000 | +6.1% |
| 2041 | 49,900,000 | +5.9% |
| 2046 | 52,910,000 | +6.0% |
| 2051 | 56,070,000 | +6.0% |
| 2056 | 59,400,000 | +5.9% |
| 2061 | 63,000,000 | +6.1% |
Modern population distribution
[edit]
By province and territory
[edit]- List of population centres in Alberta
- List of population centres in British Columbia
- List of population centres in Manitoba
- List of population centres in New Brunswick
- List of population centres in Newfoundland and Labrador
- List of population centres in the Northwest Territories
- List of population centres in Nova Scotia
- List of population centres in Nunavut
- List of population centres in Ontario
- List of population centres in Prince Edward Island
- List of population centres in Quebec
- List of population centres in Saskatchewan
- List of population centres in Yukon
By cities and municipalities
[edit]- List of largest Canadian cities by census
- List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population
First Nations
[edit]See also
[edit]- Demographics of Canada
- Canada immigration statistics
- Immigration to Canada
- Interprovincial migration in Canada
- List of Canadian provinces and territories by Human Development Index
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ McMurry, Peter H.; Shepherd, Marjorie F.; Vickery, James S. (2004). Particulate Matter Science for Policy Makers: A NARSTO Assessment. Cambridge University Press. p. 391. ISBN 978-0-521-84287-7.
- ^ "Environment – Greenhouse Gases (Greenhouse Gas Emissions per Person)". Human Resources and Skills Development Canada. 2010. Archived from the original on 27 February 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ "Population estimates quarterly". Statistics Canada. 27 March 2024. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (11 July 2018). "Canada's population clock (real-time model)". www150.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ^ "Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population". 9 February 2022. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Canadians in Context – Population Size and Growth". Human Resources and Skills Development Canada. 2010. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 17 December 2010.
- ^ a b Press, Jordan (8 February 2017). "Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver now home to one-third of Canadians: census". CTV News. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ "2016 Census: Population and dwelling counts". Statistics Canada. 8 February 2017. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ a b "Energy Efficiency Trends in Canada, 1990 to 2008". Natural Resources Canada. 2011. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ^ "Census Program Data Viewer dashboard". Statistics Canada. 9 February 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2024.
- ^ Michael R. Haines; Richard H. Steckel (2000). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- ^ a b Herbert C. Northcott; Donna Marie Wilson (2008). Dying And Death in Canada. University of Toronto Press. pp. 25–27. ISBN 978-1-55111-873-4.
- ^ Michael R. Haines; Richard H. Steckel (2000). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- ^ Garrick Alan Bailey; William C ... Sturtevant; Smithsonian Institution (U S ) (2008). Handbook of North American Indians: Indians in Contemporary Society. Government Printing Office. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-16-080388-8.
- ^ David L. Preston (2009). The Texture of Contact: European and Indian Settler Communities on the Frontiers of Iroquoia, 1667-1783. U of Nebraska Press. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-0-8032-2549-7.
- ^ William G. Dean; Geoffrey J. Matthews (1998). Concise Historical Atlas of Canada. University of Toronto Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-8020-4203-3.
- ^ R. G. Robertson (2001). Rotting Face : Smallpox and the American Indian. University of Nebraska. ISBN 978-0-87004-497-7.
- ^ a b c Hassel, Georg (1824). Statistischer Umriß der sämmtlichen europäischen und der vornehmsten außereuropäischen Staaten, in Hinsicht ihrer Entwickelung, Größe, Volksmenge, Finanz- und Militärverfassung, tabellarisch dargestellt; Zweiter Heft... Verlag des Geographischen Instituts Weimar. p. 59.
- ^ a b c d e "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Aboriginal peoples". Statistics Canada. 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ a b c Donaldson, Thomas (1886). The George Catlin Indian Gallery in the U.S. National Museum. Washington: Government Printing Office. pp. 910–915.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (25 October 2017). "The Daily — Aboriginal peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census". www150.statcan.gc.ca.
- ^ "Canada's Indigenous population". Statistics Canada. 21 June 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2024.
- ^ "Canada's Indigenous population". Statistics Canada. 21 June 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- ^ David L. Preston (2009). The Texture of Contact: European and Indian Settler Communities on the Frontiers of Iroquoia, 1667-1783. U of Nebraska Press. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-8032-2549-7.
- ^ John Powell (2009). Encyclopedia of North American Immigration. Infobase Publishing. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-4381-1012-7.
- ^ Thomas F. McIlwraith; Edward K. Muller (2001). North America: The Historical Geography of a Changing Continent. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 72. ISBN 978-1-4616-3960-2.
- ^ a b Yves Landry (1993). "Fertility in France and New France: The Distinguishing Characteristics of Canadian Behavior in the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries". Social Science History. 17 (4). Université de Montréal: 577–592, quote p 586. doi:10.1017/S0145553200016928. JSTOR 1171305. S2CID 147651557.
- ^ a b "North America's First Census". Statistics Canada. 2009. Archived from the original on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Ttables of census data collected in 1665 and 1666 by Jean Talon". Statistics Canada. 2009. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ "Estimated population of Canada, 1605 to present". Statistics Canada. 2009. Retrieved 26 August 2010.
- ^ Peter M. Leslie (1988). Ethnonationalism in a Federal State: The Case of Canada. Queen's University. p. 6 note 5. ISBN 978-0-88911-456-2.
- ^ Louis Hartz (1969). The Founding of New Societies: Studies in the History of the United States, Latin America, South Africa, Canada, and Australia. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 231. ISBN 0-547-97109-5.
- ^ Liberty's Exiles: American Loyalists in the Revolutionary World. Random House. 2012. p. 357. ISBN 9781400075478.
- ^ Jasanoff, p. 357
- ^ John M. Murrin; Paul E. Johnson; James M. McPherson; Gary Gerstle; Emily S. Rosenberg (2008). Liberty, Equality, Power, A History of the American People: To 1877. Cengage Learning. p. 172. ISBN 978-0-495-56634-2.
- ^ Elisée Reclus; Ernest George Ravenstein; Augustus Henry Keane (1893). The Earth and Its Inhabitants ...: British North America. D. Appleton. p. 479.
- ^ Donald MacKay (2009). Flight from Famine: The Coming of the Irish to Canada. Dundurn. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-77070-506-7.
- ^ a b c d Kenneth J. Rea (1991). A guide to Canadian economic history. Canadian Scholars' Press. pp. 64–65. ISBN 978-0-921627-81-4.
- ^ Patricia Wong Wong Hall; Hwang, Victor M. (2001). Anti-Asian Violence in North America: Asian American and Asian Canadian Reflections on Hate, Healing, and Resistance. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7425-0459-2.
- ^ "Estimated population of Canada, 1605 to present". Statistics Canada. 2009. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Canadians in Context – Population Size and Growth". Human Resources and Skills Development Canada. 2010. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ "History of the Census of Canada". Statistics Canada. 2006. Archived from the original on 7 May 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "OGSPI 1911 Census Menu". The Ontario Genealogical Society (OGS). 2005. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ "Canadian Immigration – Early 1900s". British immigrants in Montreal. 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ "By definition: Boom, bust, X and why". The Globe and Mail. 2006–2009. Archived from the original on 20 May 2009. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Census of Canada, A population and dwelling counts" (PDF). Statistics Canada. 1997. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "2001 Census facts: did you know..." (PDF). Statistics Canada. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ "Population estimates". Statistics Canada. 2006. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Differences between Statistics Canada's census counts and population estimates" (PDF). Statistics Canada. 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts A portrait of the Canadian population". Statistics Canada. 2007. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "The Constitution Act, 1867". The Solon Law Archive. 2001. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ "The World FactBook – Canada", The World Factbook, 2022
- ^ "Canada Population 2022", World Population Review
- ^ "Immigration overview – Permanent and temporary residents". Citizenship and Immigration Canada. 2012. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ "Immigration fuels Canada's largest population growth of over 1 million". BBC News. 23 March 2023. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Summaries of census information from 1605 to 1871" (PDF). Statistics of Canada. 2008. Retrieved 20 July 2010.
- ^ "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Early exploration (16th century)". Statcan.gc.ca. 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ Linda S. Cordell; Kent Lightfoot; Francis McManamon; George Milner (30 December 2008). Archaeology in America: An Encyclopedia: An Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. pp. 82–. ISBN 978-0-313-02189-3.
- ^ Annette Kolodny (2012). In Search of First Contact: The Vikings of Vinland, the Peoples of the Dawnland, and the Anglo-American Anxiety of Discovery. Duke University Press. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-8223-5286-0.
- ^ a b Conrad Heidenreich; K. Janet Ritch (2010). Samuel de Champlain Before 1604: Des Sauvages and Other Documents Related to the Period. McGill-Queen's Press – MQUP. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-0-7735-3757-6.
- ^ René Chartrand (2008). The Forts of New France in Northeast America 1600-1763. Osprey Publishing. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-84603-255-4.
- ^ a b Alan Gordon (2010). The Hero and the Historians: Historiography and the Uses of Jacques Cartier. UBC Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-7748-5920-2.
- ^ Britannica Educational Publishing (2011). From Columbus to Colonial America: 1492 to 1763. Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-61530-734-0.
- ^ "Canadian Military Heritage". Cmhg.gc.ca. 2011. Archived from the original on 25 December 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ a b c d Roger E. Riendeau (2007). A Brief History of Canada. Infobase Publishing. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-4381-0822-3.
- ^ John G. Reid (2004). The "conquest" of Acadia, 1710: Imperial, Colonial, and Aboriginal Constructions. University of Toronto Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-8020-8538-2.
- ^ a b Harald E. L. Prins (1996). The Miʼkmaq: resistance, accommodation, and cultural survival. Harcourt Brace College Pub. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-03-053427-0.
- ^ "Early French settlements (1605 to 1691)". Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "Early French settlements (1605 to 1691)". Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "Introduction to Censuses of Canada, 1665 to 1871" (PDF). Retrieved 20 October 2024.
- ^ "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Early French settlements (1605 to 1691)". Statistics Canada. 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ "Early French settlements (1605 to 1691)". Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ a b "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Early English settlements (1692 to 1749)". Statistics Canada. 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ Spencer C. Tucker (2012). Almanac of American Military History. ABC-CLIO. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-59884-530-3.
- ^ Ruben C. Bellan (2003). Canada's Cities: A History. Whitefield Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-9699686-1-0.
- ^ Andrew Ross; Andrew Smith (2011). Canada's Entrepreneurs: From The Fur Trade to the 1929 Stock Market Crash: Portraits from the Dictionary of Canadian Biography. University of Toronto Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-4426-6254-4.
- ^ Shannon Lewis-Simpson; Peter E. Pope (2013). Exploring Atlantic Transitions: Archaeologies of Transience and Permanence in New Found Lands. Boydell & Brewer Ltd. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-84383-859-3.
- ^ "The Governor General of Canada > 400th Anniversary of the town of Cupids". Gg.ca. 17 August 2010. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ Jerry Bannister (2003). The Rule of the Admirals: Law, Custom, and Naval Government in Newfoundland, 1699-1832. University of Toronto Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-8020-8613-6.
- ^ Census of Canada 1851/52-. Des presses a Vapeur de Lovell et Lamoureaux. 1876. p. 16.
- ^ a b c Michael R. Haines; Richard H. Steckel (2000). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- ^ a b Canada. Dept. of Public Works (1891). Annual Report. Toronto. pp. 3–.
- ^ Raymonde Litalien (2004). Champlain: The Birth of French America. McGill-Queen's Press. p. 368. ISBN 978-0-7735-7256-0.
- ^ Terence J. Fay (2002). History of Canadian Catholics. McGill-Queen's Press. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-7735-2313-5.
- ^ James Pritchard (2004). In Search of Empire: The French in the Americas, 1670-1730. Cambridge University Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-521-82742-3.
- ^ "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Upper Canada & Loyalists (1785 to 1797)". Statistics Canada. 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ Rocío G. Davis; Rosalía Baena (2000). Tricks with a Glass: Writing Ethnicity in Canada. Rodopi. p. 113. ISBN 90-420-1213-7.
- ^ "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: The 1800s (1806 to 1871)". Statistics Canada. 2008. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ a b c "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Estimated population of Canada, 1605 to present". Statistics Canada. 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (28 September 2022). "Population estimates on July 1st, by age and sex". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- ^ "Censuses of Canada 1665 to 1871: Aboriginal peoples". www150.statcan.gc.ca.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (3 April 2013). "The aboriginal population and the Census : 120 years of information, 1871-1991 / Gustave Goldmann". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (3 April 2013). "1961 Census of Canada : population : vol. I - part 2 = 1961 Recensement du Canada : population : vol. I - partie 2. Ethnic groups". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (3 April 2013). "1971 Census of Canada : population : vol. I - part 3 = Recensement du Canada 1971 : population : vol. I - partie 3. Ethnic groups". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (3 April 2013). "1991 employment equity data highlights". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (4 June 2019). "Data tables, 1996 Census Total Population by Age Groups (11) and Sex (3), Showing Aboriginal Groups (8), for Canada, Provinces, Territories and Census Metropolitan Areas, 1996 Census (20% Sample Data)". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (23 December 2013). "2001 Census Topic-based tabulations Aboriginal Identity (8), Age Groups (11B) and Sex (3) for Population, for Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2001 Census - 20% Sample Data". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (1 May 2020). "2006 Census Topic-based tabulations Aboriginal Identity (8), Sex (3) and Age Groups (12) for the Population of Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2006 Census - 20% Sample Data". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (23 January 2019). "2011 National Household Survey: Data tables Aboriginal Identity (8), Age Groups (20), Registered or Treaty Indian Status (3) and Sex (3) for the Population in Private Households of Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2011 National Household Survey". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (17 June 2019). "Aboriginal Identity (9), Age (20), Registered or Treaty Indian Status (3) and Sex (3) for the Population in Private Households of Canada, Provinces and Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2016 Census - 25% Sample Data". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (21 September 2022). "Indigenous identity by Registered or Treaty Indian status: Canada, provinces and territories, census metropolitan areas and census agglomerations with parts". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Belshaw, John Douglas (17 May 2016). "11.3 Natives by the Numbers". www.opentextbc.ca. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ^ "Canada Year Book 1932" (PDF). Statistics Canada. 2009. p. 91. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ "Canada Year Book 1955". Statistics Canada. 2009. p. 135. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ "Canada Year Book 1967". Statistics Canada. 2009. p. 184. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ Population and private dwellings occupied by usual residents and intercensal growth for Canada – 1971 to 2011. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2014
- ^ Manitoba (Canada): Province & Major Cities – Statistics & Maps on City Population. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2014
- ^ 1996 Census of Canada – Electronic Area Profiles. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2014
- ^ Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories – 2006 and 2001 censuses. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2014
- ^ Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories – 2011 and 2006 censuses. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2014
- ^ Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories – 2016 and 2011 censuses. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 8 February 2017
- ^ a b "Population Projections for Canada - Components of population growth, high-growth scenario - 2009/2010 to 2060/2061" (PDF). Statistics Canada. Catalogue no. 91-520. 2006. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ^ Harris, Kathleen (30 October 2020). "government plans to bring in more than 1.2M immigrants in next 3 years". CBC.
Further reading
[edit]- Roderic P. Beaujot; Don Kerr (2007). The changing face of Canada: essential readings in population. Canadian Scholars' Press. ISBN 978-1-55130-322-2.
- Michael R. Haines; Richard H. Steckel (2000). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- Alan Simmons (2010). Immigration and Canada: Global and Transnational Perspectives. Canadian Scholars' Press. ISBN 978-1-55130-362-8.
External links
[edit]- Canada's population clock – Statistics Canada
- Canada Population – Worldometers
- Annual Estimates of Population for Canada, Provinces and Territories, from July 1, 1971 to July 1, 2014 – Economics and Statistics Branch (Newfoundland & Labrador Statistics Agency)
- Population and Dwelling Count, 2011 Census – Statistics Canada
- Population estimates and projections, 2010 – 2036 – Statistics Canada
- Historical population and migration statistical data – Statistics Canada (Archived)
- Population Institute of Canada
